Are there alternatives to CPAP therapy? Yes
- Oral Appliance - Dental Device (TAP)
- An oral appliance is an effective treatment option for people with mild to moderate OSA who either prefer it to CPAP or are unable to successfully comply with CPAP therapy. Oral appliances look much like sports mouth guards, and they help maintain an open and unobstructed airway by repositioning or stabilizing the lower jaw, tongue, soft palate or uvula. Some are designed specifically for snoring, and others are intended to treat both snoring and sleep apnea. They should always be fitted by dentists who are trained in sleep medicine.


- Positional Therapy- Zzoma
- A treatment used for patients suffering from mild OSA. Patients are advised to stay off of the back while sleeping and raise the head of the bed to reduce symptoms.


- Over-the-counter remedies

- Behavioural changes

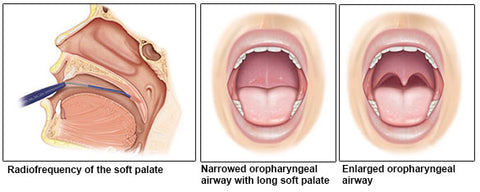
- Surgery